Introduction
You’ve probably heard of blockchain—the technology that powers everything from cryptocurrencies to secure data storage solutions. But have you ever wondered where all this blockchain data is actually stored? Understanding the storage aspects can help you better grasp the technology’s capabilities and limitations. So, let’s dig in!
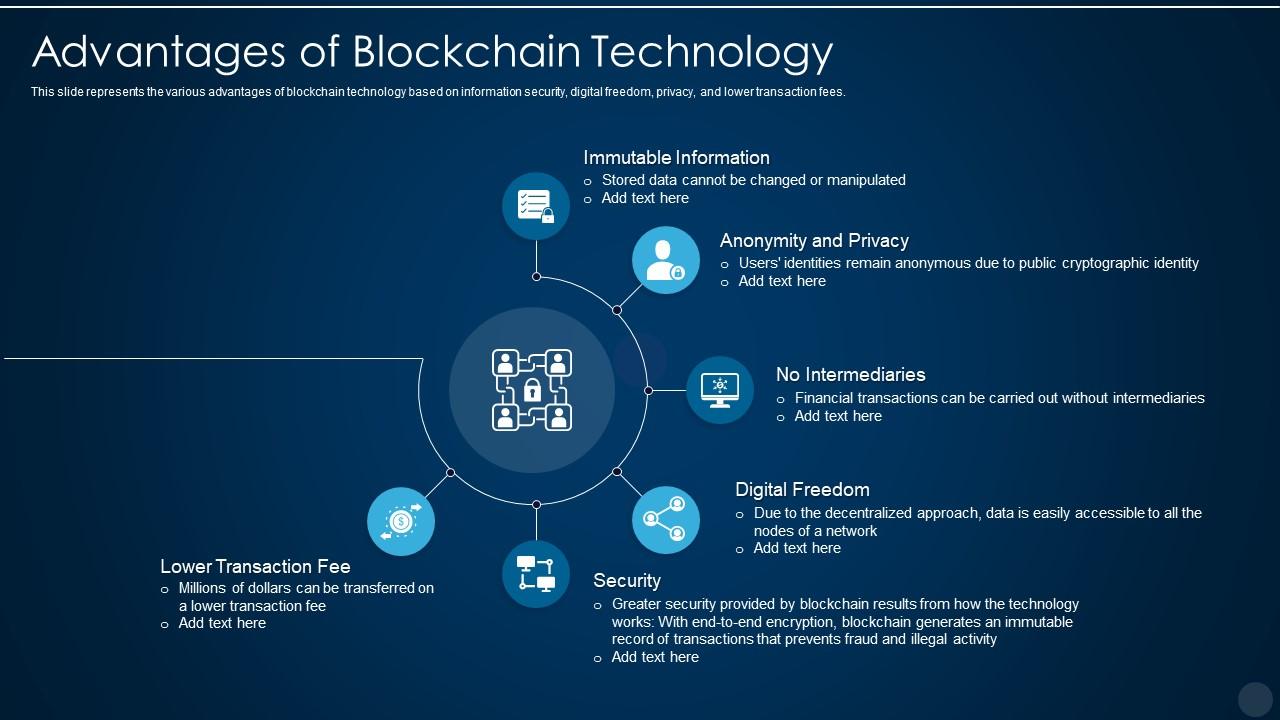
What Is Blockchain?
Definition
At its core, a blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions in a decentralized manner. Unlike a centralized database, the blockchain isn’t stored in a single location but rather distributed across multiple nodes.
Use Cases
From powering Bitcoin to securing medical records, blockchain is a versatile technology with a broad range of applications.
Basic Components of Blockchain
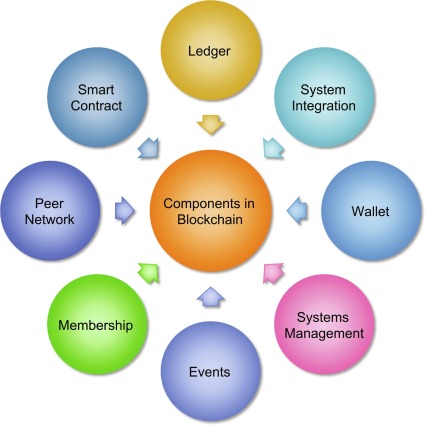
Blocks
The basic unit of a blockchain is a block, which contains transaction data and other metadata.
Chain
These blocks are interconnected, forming a chronological “chain,” hence the name blockchain.
Network
The blockchain exists within a network of nodes that validate and record transactions.
Decentralization: The Key Principle
A decentralized network eliminates the need for a central authority, enhancing security and reducing the risk of data manipulation.
Nodes: The Building Blocks
Full Nodes
These are computers that store a complete copy of the blockchain.
Light Nodes
Light nodes store only essential information, providing a quicker but less detailed view of the blockchain.
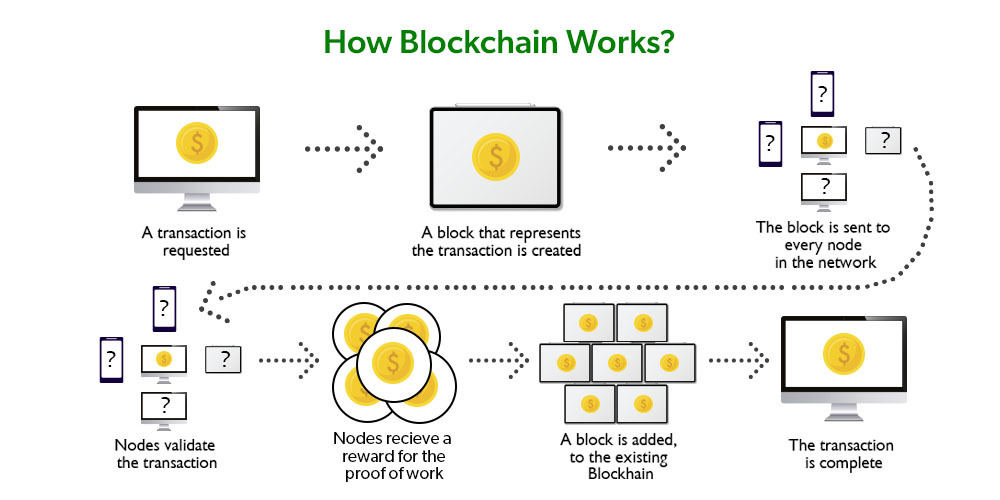
How Are Transactions Stored?
Each transaction is verified and then added to a block. Once a block is full, it is attached to the existing chain.
Where Is the Blockchain Physically Stored?
The blockchain is stored on the hard drives of the nodes participating in its network.
Cloud Storage vs Local Storage
Pros and Cons
Cloud storage offers scalability but may compromise on security. Local storage is secure but less scalable.
What Happens When a Node Goes Offline?
The blockchain remains operational, as other nodes maintain the ledger.
Security Measures
Encryption
Blockchain employs encryption algorithms for security.
Consensus Mechanisms
These mechanisms, like Proof of Work, ensure that all nodes agree on the validity of transactions.
Real-World Examples
Bitcoin
The Bitcoin blockchain is stored across thousands of nodes globally.
Ethereum
Ethereum’s blockchain also uses decentralized storage, adding functionalities like smart contracts.
Future of Blockchain Storage
With innovations like sharding and off-chain storage, the future of blockchain storage looks promising.
Conclusion
Understanding where the blockchain is stored can provide insights into its security, scalability, and robustness. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, so will its storage solutions, opening up new possibilities and applications.
FAQs
- Where is blockchain data stored?
- On the hard drives of network nodes.
- What is decentralization in blockchain?
- Elimination of central authority.
- What is a node in blockchain?
- A computer that validates and records transactions.
- How secure is blockchain storage?
- Highly secure due to encryption and consensus mechanisms.
- What’s the future of blockchain storage?
- Innovations like sharding and off-chain solutions are in the pipeline.